Navigating Brain Tumour Treatment in Singapore – How to Choose the Right Brain Surgeon
Our brains are at the core of everything we do—our thoughts, memories, movements, and even our emo
MBBS (SG)●MRCS (Edin)●IFAANS●FAMS (Neuro.Surg)●FRCS Ed (Neuro.Surg)
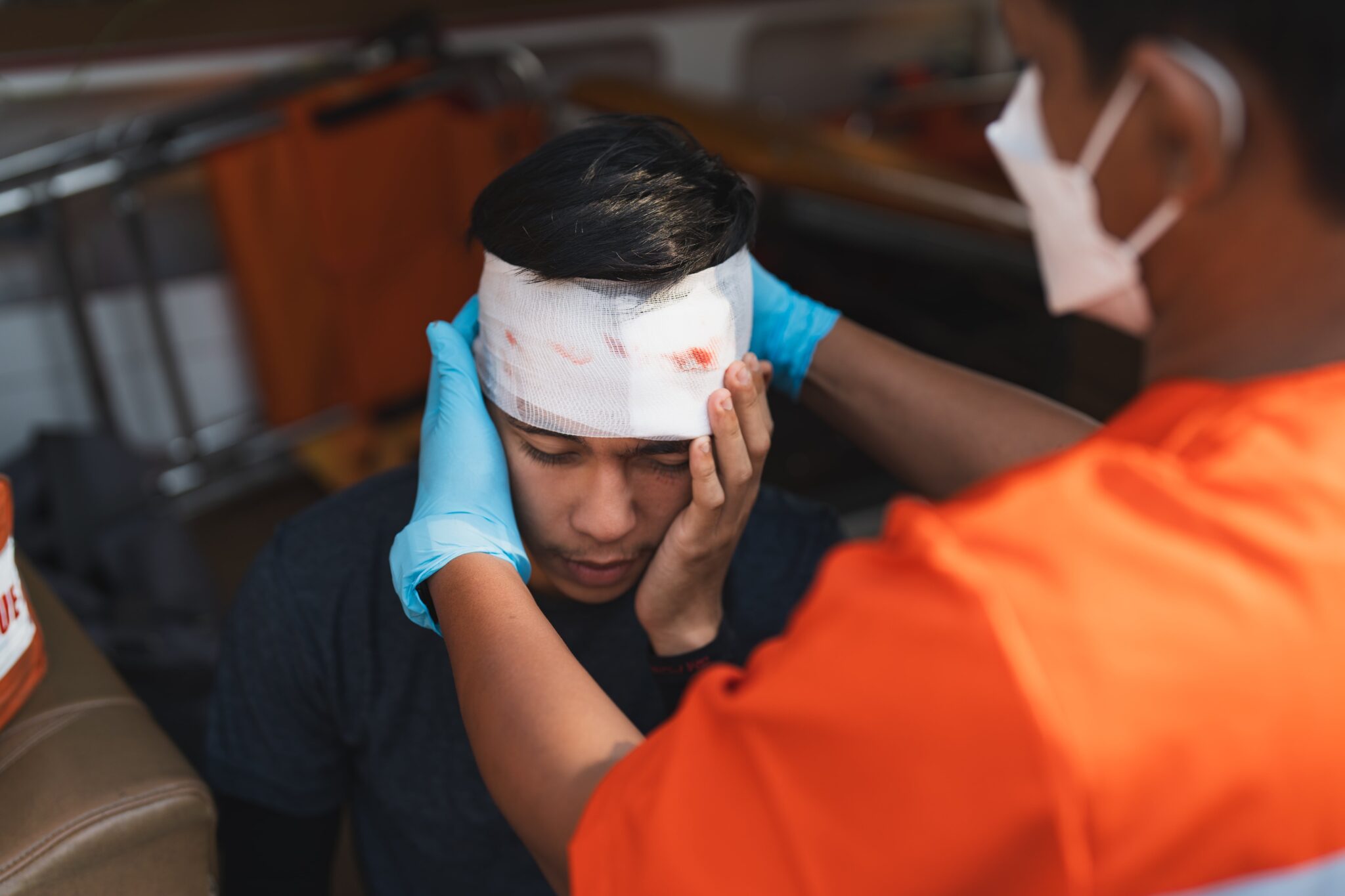
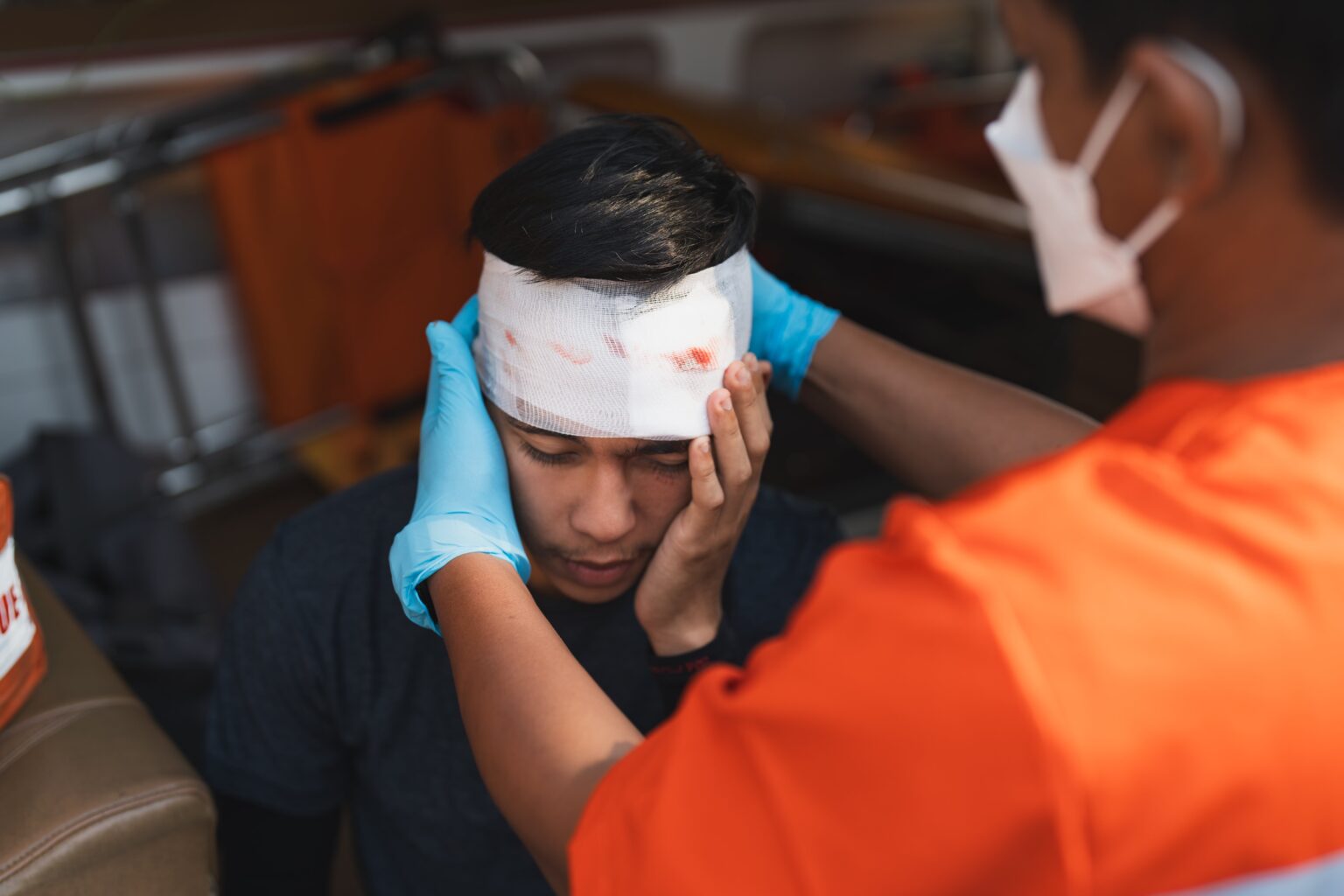
Head injuries or commonly referred to as traumatic brain injuries (TBI), refer to a traumatic experience that can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being. It is essential to seek prompt and proper treatment for TBI to prevent further complications and improve recovery. Traumatic brain injury treatment in Singapore follows a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach involving various medical specialists and healthcare professionals to provide the best possible care for patients.
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI), usually occur when there is a blow applied to the head, causing a certain degree of damage. Furthermore, rapid forward and backward movement and shaking of the head from a strong force can also cause damage to the brain tissues and blood vessels. Some common causes of TBIs include:
Depending on the severity and a patient’s Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), traumatic brain injuries are frequently classified into the following categories:
| TBI Categories | GCS score |
| Mild | 3-8 |
| Moderate | 9-12 |
| Severe | 13-15 |
Based on the GCS, the scale is scored between 3 and 15 — 3 being the worst and 15 being the best.
Mild traumatic brain injuries refer to injuries that display concussive symptoms such as temporary loss of consciousness, confusion, headache, dizziness, and nausea. Usually, such injuries resolve on their own with adequate rest and care. However, medical intervention might be required if the present symptoms worsen or persist.
Unlike mild TBIs, moderate or severe TBIs occur when a sudden force is applied to the head, causing severe damage to the brain structures (brain, skull or scalp). It is crucial to seek prompt medical care if you experience any of the following symptoms:
If the injury is left untreated, it can worsen and lead to severe consequences.

Mild, moderate and severe TBIs can lead to different complications. For instance, if a mild TBI is left untreated and there is not adequate time for the brain to heal, it increases the risk for second-impact syndrome, a life-threatening condition. This occurs when your brain suddenly swells, and your brain tissue is displaced.
Edema, or swelling of the brain, can occur after a head trauma. It is a severe condition that requires immediate medical attention to prevent further damage to the brain and potentially life-threatening complications. When this happens, the skull may be unable to accommodate the swelling, causing increased pressure inside the brain.
However, for moderate or severe TBIs, it can lead to long-term consequences including:
Haemorrhage is a medical term used to describe bleeding from damaged blood vessels. Brain injuries can cause bleeding in and around the brain, which can lead to increased pressure and damage to brain tissue. Depending on the severity and location of the bleeding, it can be life-threatening.
Subarachnoid haemorrhages frequently result in headaches and vomiting, while the severity of intracerebral haemorrhages hinges on the volume of bleeding. However, over time, any quantity of blood may lead to increased pressure.
When the brain is given enough time to heal, the brain cells can regenerate. However, in the event the brain does not have enough time to heal, it can affect the different cognitive and motor functions of the body. For instance, changes in the cognitive skills or loss of certain motor abilities.
Post traumatic hydrocephalus occurs when damage to the brain causes the brain tissues around the ventricles to shrink. To fill in the extra space, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the ventricles causing it to be enlarged, putting pressure on the brain tissues. Thus, leading to an accumulation of CSF in the brain.

The approach to treating TBIs varies, depending on the injury’s type and severity. For minor brain injuries, symptoms may be limited to pain at the injury site and self-limiting
Even with seemingly minor injuries, monitoring your condition closely is crucial to prevent it from deteriorating. Contrary to popular belief, sleeping after sustaining a TBI is not inherently dangerous.
However, it is advisable to be awakened every couple of hours to check for new symptoms. Should you experience any new or worsening symptoms, a prompt visit to the doctor is necessary.
For severe TBIs, hospitalisation may be necessary. The treatment administered will be customised according to your unique diagnosis, guaranteeing optimal care and facilitating the best possible recovery journey. The treatment for severe TBIs may include the following:
Various medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and aid in recovery. These may include anticonvulsants to prevent seizures or diuretics to reduce pressure on the brain and pain killers to help treat the headaches.
In some cases, surgery may be required to reduce swelling or remove blood clots or damaged tissue from the brain. This type of treatment is typically reserved for severe traumatic brain injuries. Once the patient is stable, surgery may be performed to repair skull fractures or correct any damage to the brain. For instance, ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion to treat the hydrocephalus.

Sustaining traumatic brain injuries and recovering from it can be daunting, but you don’t have to face it alone. At Precision Neurosurgery, we not only understand the complexities of traumatic brain injuries but also offer a supportive hand throughout your journey. With our extensive experience in treating traumatic brain injuries, we are committed to providing personalised care and tailoring treatments to meet each patient’s unique needs.
If you suspect that you have sustained a head injury, book an appointment with us for an extensive and thorough evaluation to help put your worries at ease.
Consult with Dr Teo for a comprehensive evaluation and a personalized treatment plan.


Dr Teo Kejia is an experienced Senior Consultant Neurosurgeon and Director at Precision Neurosurgery.
Dr Teo has extensive knowledge and experience in the field of neurosurgery, with a particular focus on complex brain tumour procedures. He is adept in employing advanced surgical techniques, including brain mapping and awake brain surgery, especially for treating gliomas and glioblastomas. His expertise extends to neuro-oncology, encompassing both brain and spinal tumours, as well as neurovascular and skull base surgery.
Additionally, Dr Teo offers treatment for a range of neurological conditions, such as traumatic head injuries, intracerebral aneurysms, and degenerative spine disorders, which include neck and back pain. He is also proficient in managing ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes, hydrocephalus, trigeminal neuralgia, and hemifacial spasm.
Got Questions? Please fill in the enquiry form below and we look forward to addressing your question.